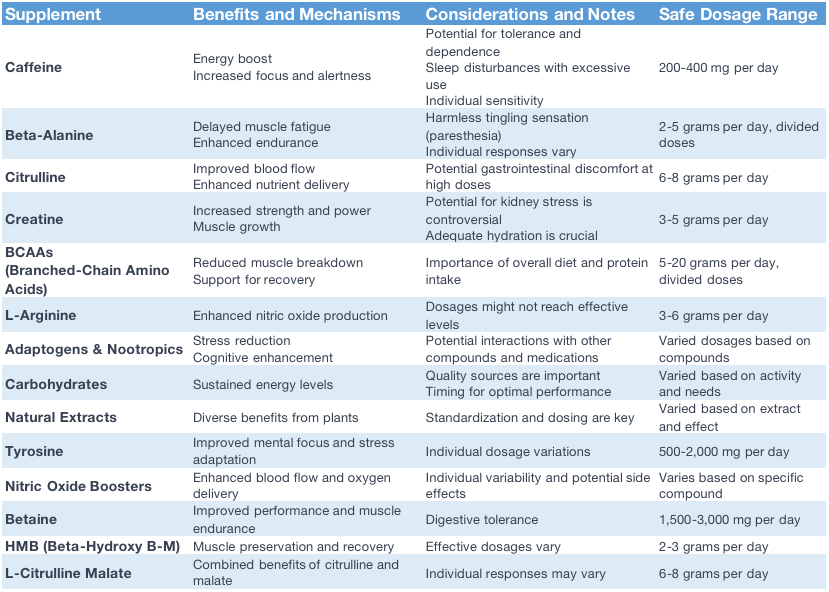
In the dynamic world of sports, fitness and exercise, the quest for enhanced performance and optimal results is a perpetual journey. Pre-workout supplements have emerged as a popular tool in this pursuit, promising to elevate workout sessions to new heights. These supplements, often formulated with a blend of specific compounds, hold the potential to boost energy, focus, endurance, and even muscle pumps, making them an intriguing addition to many athletes’ routines. This blog aims to unravel the intricate world of pre-workout compounds, delving into their diverse effects, advantages, disadvantages, associated risks, medical considerations, safe dosages, and recommended usage duration.
As fitness enthusiasts and athletes seek that extra edge during workouts, the realm of pre-workout compounds offers a vast landscape of choices, each with its unique mechanisms and potential benefits. From caffeine’s renowned ability to provide an instant surge of energy and alertness to amino acids like beta-alanine that help battle fatigue, the array of compounds available presents a tapestry of possibilities for optimizing exercise performance. Moreover, the inclusion of adaptogens, nootropics, carbohydrates, and natural extracts adds layers of complexity and versatility, catering to different preferences and fitness goals.
While the promise of heightened performance is enticing, it’s crucial to navigate the world of pre-workout compounds with caution and informed decision-making. With potential drawbacks like jitters, insomnia, and individual tolerances to consider, understanding the risks associated with each compound is essential. Furthermore, certain medical conditions demand careful consideration, as the interaction between pre-existing health concerns and these supplements could yield unintended consequences.
Caffeine: Energizing Your Workouts:
Caffeine is one of the most widely recognized and utilized pre-workout compounds, known for its ability to provide an instant boost in energy, focus, and alertness. It’s a natural stimulant found in various sources, such as coffee beans, tea leaves, and cacao. When consumed before a workout, caffeine can have several positive effects on performance and overall exercise experience.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Alertness: Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system, leading to heightened alertness and reduced perceived effort during workouts. This effect can be particularly beneficial for early morning or high-intensity training sessions.
- Increased Energy: By blocking the action of adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes sleep and relaxation, caffeine increases the release of other neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine. This results in a surge of energy and a feeling of wakefulness.
- Improved Endurance: Caffeine has been shown to enhance endurance performance by increasing the body’s ability to utilize fat as an energy source. This can lead to a delay in the onset of fatigue during prolonged workouts.
- Mental Focus: The cognitive-enhancing effects of caffeine can improve mental clarity and focus, allowing you to concentrate better on your training routine.
Risks and Considerations:
- Jitters and Restlessness: Consuming too much caffeine can lead to feelings of restlessness, nervousness, and jitters. These sensations might be uncomfortable and potentially affect workout performance.
- Insomnia: Since caffeine is a stimulant, consuming it too close to bedtime can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to insomnia. It’s recommended to avoid caffeine in the evening or at least several hours before bedtime.
- Individual Tolerance: People vary in their sensitivity to caffeine. Some individuals may experience its effects more strongly than others, leading to variations in response and tolerance levels.
- Cardiovascular Effects: High doses of caffeine can temporarily increase heart rate and blood pressure. Individuals with underlying heart conditions should consult a healthcare professional before consuming caffeine-containing pre-workout supplements.
Medical Considerations:
- Individuals with heart conditions, hypertension, or anxiety disorders should be cautious when using caffeine as a pre-workout supplement. Consulting a healthcare provider before use is advisable.
- Pregnant women and individuals who are sensitive to caffeine should also approach its use with caution.
Safe Dosage
- The safe dosage of caffeine varies depending on an individual’s tolerance, but moderate doses between 100-200 mg are commonly used as pre-workout supplements.
- Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing can help gauge personal sensitivity and avoid potential side effects.
Also Read: Coffee Health Benefits & Sife Effects
Beta-Alanine: Fighting Fatigue and Enhancing Endurance:
When it comes to pushing through intense workouts and extending the boundaries of endurance, beta-alanine emerges as a notable pre-workout compound. This amino acid, often found in dietary sources like meat and poultry, plays a pivotal role in combating muscle fatigue and enabling athletes to perform at their peak for longer durations.
Benefits:
- Delaying Muscle Fatigue: Beta-alanine is a precursor to carnosine, a molecule that helps buffer the buildup of lactic acid in muscles during high-intensity exercise. By reducing the accumulation of lactic acid, beta-alanine can delay the onset of muscle fatigue, allowing you to push through challenging workouts.
- Improved Endurance: With its fatigue-delaying properties, beta-alanine contributes to enhanced endurance during aerobic and anaerobic activities. This is particularly beneficial for athletes engaged in activities like sprinting, interval training, and weightlifting.
Risks and Considerations:
- Tolerance and Timing: It’s important to note that the effects of beta-alanine are cumulative. Regular consumption over a period of weeks is necessary to achieve noticeable benefits. Starting supplementation well in advance of an event or competition is advisable.
- Tingling Sensation: One distinctive characteristic of beta-alanine consumption is the harmless tingling sensation, known as paresthesia, experienced in the skin. While some individuals find this sensation uncomfortable, it’s a transient effect and doesn’t pose any harm. Individuals sensitive to this sensation might opt for slower-release formulations or divide their daily dose.
Medical Considerations:
- Individuals with kidney disorders should consult a healthcare professional before using beta-alanine, as higher doses might increase the workload on the kidneys.
Safe Dosage:
- The most commonly studied dosage range is between 2 to 5 grams of beta-alanine per day.
- To minimize or spread out the tingling sensation, some individuals choose to split their daily dose into smaller amounts taken throughout the day.
It’s important to be patient with beta-alanine, as its benefits become more pronounced with consistent use over time. Consulting a healthcare provider, especially if you have kidney concerns, will help ensure that beta-alanine is a suitable addition to your pre-workout routine.
Citrulline: Pumping Up Blood Flow and Muscle Pumps:
Among the list of pre-workout compounds, citrulline stands out for its role in enhancing blood flow, promoting vasodilation, and delivering those coveted muscle pumps. Derived from sources like watermelons and other fruits, citrulline has gained popularity for its potential to optimize nutrient delivery to muscles and amplify workout performance. L-citrulline malate is an intriguing fusion of two distinct elements, each offering unique advantages. This compound, born from the marriage of L-citrulline and malic acid, embodies a potential synergistic powerhouse that holds promise for enhancing exercise performance and pushing physical boundaries.
L-citrulline is renowned for its role in promoting the production of nitric oxide, a vasodilator that widens blood vessels and improves blood flow and thus fosters increased nutrient delivery to muscles, contributing to enhanced endurance and muscle function. Malic acid, also known as malate, plays a key role in the Krebs cycle, the body’s energy production pathway. By participating in this cycle, malate assists in generating adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cellular energy currency. The potential reduction of exercise-induced fatigue is a consequence of improved ATP production.
Synergistic Effects: The combination of L-citrulline and malate appears to create a harmonious interplay that magnifies their individual benefits. The vasodilation induced by L-citrulline is complemented by the enhanced energy production facilitated by malate. This synergy has the potential to amplify both endurance and strength during workouts, forging a path toward improved overall performance
Benefits:
- Enhanced Blood Flow: Citrulline’s primary mechanism of action involves increasing nitric oxide production, leading to vasodilation and improved blood flow. This effect can benefit athletes by enhancing oxygen and nutrient delivery to working muscles.
- Muscle Pumps: Vasodilation not only supports nutrient delivery but also leads to the “pump” sensation in muscles during exercise. This not only boosts motivation but may also contribute to muscle growth over time.
- Endurance Benefits: Improved blood flow can aid in reducing muscle fatigue during workouts, potentially leading to enhanced endurance and prolonged workout capacity.
Risks and Considerations:
- Gastrointestinal Discomfort: High doses of citrulline may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, including symptoms like bloating and diarrhea. Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing can help mitigate this risk.
Medical Considerations:
- Individuals with low blood pressure should exercise caution with citrulline supplementation, as the compound’s vasodilatory effects could potentially lead to further drops in blood pressure.
Safe Dosage:
- A common dosage range for citrulline supplementation is between 6 to 8 grams per day.
- Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing can help minimize potential gastrointestinal discomfort.
Also Read: Gym, Cardio or Yoga? Which is better?
Creatine: Powering Strength and Muscle Growth:
When it comes to pre-workout compounds that have stood the test of time, creatine takes centre stage. This naturally occurring compound, found in meat and fish, has been extensively studied and is renowned for its ability to enhance strength, power, and muscle growth.
Benefits:
- Increased ATP Production: Creatine functions as a rapid source of energy by replenishing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecule responsible for powering muscular contractions. This results in improved short-term bursts of energy, which can be particularly advantageous for high-intensity activities.
- Strength and Power: With increased ATP availability, creatine supplementation is associated with improved performance in strength-focused exercises such as weightlifting and sprinting.
- Muscle Growth: Creatine’s role in enhancing cellular hydration and promoting protein synthesis contributes to muscle growth over time. This is particularly valuable for individuals seeking gains in muscle mass.
Risks and Considerations:
- Water Retention: Creatine’s mechanism of action involves drawing water into muscle cells, which can lead to temporary water retention and a slight increase in body weight. This effect is harmless and contributes to the muscle fullness associated with creatine use.
- Kidney Function: While creatine is generally safe for healthy individuals, those with preexisting kidney issues should consult a healthcare professional before use, as high doses may exacerbate kidney stress.
Medical Considerations:
- Individuals with kidney disorders should approach creatine use cautiously, as high doses could potentially strain kidney function.
- Some rare genetic conditions may contraindicate creatine supplementation. Consulting a healthcare provider is recommended.
Safe Dosage:
- A common practice of loading creatine involves consuming around 20 grams of creatine per day for the first 5-7 days, followed by a maintenance phase of 3-5 grams per day. However, we recommend skipping this loading phase and instead consuming 3 – 5 grams per day for a reasonable duration to benefit from the supplementation.
Also Read: Creatinine & Kidney Health
BCAAs (Branched-Chain Amino Acids): Supporting Recovery and Muscle Preservation:
In the context of pre-workout compounds, branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) have drawn interest due to their potential to aid in recovery, reduce muscle breakdown, and assist in maintaining muscle integrity after workouts. The effectiveness of BCAAs is a topic of discussion and varies among experts, contributing to differing viewpoints on their impact. BCAAs consist of three essential amino acids: leucine, isoleucine, and valine. These amino acids play a role in muscle protein synthesis and energy production during exercise. However, whether BCAAs provide significant benefits for everyone remains a topic of contention
Benefits:
- Muscle Recovery: BCAAs, including leucine, isoleucine, and valine, play a crucial role in muscle protein synthesis, the process by which muscles repair and grow after exercise. It is hence believed that consuming BCAAs before or during workouts can facilitate quicker recovery. However, this is a highly contentious and debated topic.
- Reduced Muscle Breakdown: BCAAs are particularly valuable for individuals in a calorie deficit or engaging in fasted training. They can help prevent the breakdown of muscle tissue for energy, preserving hard-earned gains.
- Endurance and Performance: Some studies suggest that BCAAs may reduce perceived effort during endurance exercises, potentially enhancing workout performance.
Risks and Considerations:
- Balanced Diet vs. Supplementation: While BCAAs can be beneficial for those with specific dietary restrictions, individuals consuming a well-rounded diet may already obtain sufficient BCAAs from food sources. In such a case, consuming BCAA is a complete waste of money
- Individual Needs: Not everyone may require BCAA supplementation, as other amino acids also play important roles in muscle growth and recovery.
Medical Considerations:
- BCAA supplementation is generally safe for healthy individuals. However, those with certain medical conditions, such as branched-chain ketoaciduria, should consult a healthcare professional.
Safe Dosage:
- Dosages vary based on individual goals and training intensity. Consuming around 5-10 grams of BCAAs before or during workouts is a common practice.
Also Read: Supplement Interaction with Medicines
L-Arginine: Enhancing Nitric Oxide Production:
Among the array of pre-workout compounds, L-arginine stands out for its role in boosting nitric oxide production, which in turn leads to improved blood flow and vascular function. This amino acid, naturally found in protein-rich foods, has garnered attention for its potential benefits in enhancing workout performance.
Benefits:
- Nitric Oxide Production: L-arginine serves as a precursor to nitric oxide, a molecule that relaxes and widens blood vessels, leading to vasodilation. This effect enhances blood flow and nutrient delivery to muscles, contributing to improved exercise performance.
- Vascular Health: Beyond its workout-related benefits, L-arginine’s ability to support vascular function can have long-term implications for overall cardiovascular health.
- Muscle Pump and Nutrient Delivery: By increasing blood flow, L-arginine can lead to better muscle pumps during workouts and improved nutrient delivery, potentially aiding in recovery.
Risks and Considerations:
- Individual Variability: L-arginine’s effectiveness can vary among individuals, as its conversion to nitric oxide depends on several factors, including genetics and existing nitric oxide production.
- Tolerance and Dosage: Some individuals might develop tolerance to L-arginine’s effects over time, requiring higher dosages to achieve the same benefits.
Medical Considerations:
- Individuals with herpes viruses or those prone to cold sores should be cautious with L-arginine supplementation, as it might exacerbate outbreaks.
- L-arginine is not suggested for people who have low blood pressure problems; the vasodilation of blood vessels may further drop the blood pressure.
- L-arginine may interact with certain medications, including blood pressure medications and erectile dysfunction drugs. Consultation with a healthcare professional is advised.
Safe Dosage:
- A common dosage range for L-arginine supplementation varies from 2 to 6 grams per day.
- Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing can help gauge individual responsiveness.
Also Read: Aerobic Vs Anaerobic Exercises
Adaptogens and Nootropics: Stress Management and Cognitive Boost:
In the ever-evolving landscape of pre-workout compounds, the inclusion of adaptogens and nootropics brings a new dimension to enhancing both physical and mental performance. These compounds, often derived from plants, have gained attention for their potential to manage stress, improve focus, and optimize cognitive function during workouts.
Adaptogens:
- Stress Response: Adaptogens like ashwagandha, rhodiola, and ginseng are known for their ability to help the body adapt to stressors, be they physical, emotional, or environmental. By regulating stress hormones like cortisol, they can contribute to a more balanced stress response during intense workouts.
- Endurance and Recovery: Some adaptogens are believed to enhance endurance by improving oxygen utilization and reducing oxidative stress, potentially leading to better workout capacity and recovery.
Nootropics:
- Cognitive Enhancement: Nootropics, also known as “smart drugs,” encompass compounds like L-theanine, tyrosine, and huperzine-A. These compounds are believed to enhance cognitive function, memory, and focus, making them valuable additions to pre-workout formulations.
- Reduced Mental Fatigue: Nootropics can counteract mental fatigue and help maintain alertness during prolonged workouts, ensuring that both mind and body are primed for performance.
Risks and Considerations:
- Individual Responses: The effects of adaptogens and nootropics can vary among individuals. Personal experimentation might be necessary to identify the most effective compounds and dosages for your body.
- Interactions and Stacking: Some adaptogens and nootropics may interact with medications such as antihypertensives, antidepressants and antiepileptic drugs. It may have synergistic effects when combined with certain other compounds. Consulting a healthcare provider or qualified expert is recommended in such cases.
Medical Considerations:
- Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or mood disorders, should exercise caution and seek professional guidance before using adaptogens and nootropics.
- Excessive use of these may cause liver damage
Safe Dosage:
- Dosages of adaptogens and nootropics can vary widely based on the specific compound and its intended effects.
- Consulting product labels, reputable sources, and healthcare professionals can help determine suitable dosages.
Also Read: Ashwagandha – Benefits & Side Effects
Carbohydrates: Sustaining Energy Levels:
Carbohydrates play a fundamental role in providing a sustained and readily available source of energy for optimal workout performance. While often overshadowed by other compounds, the inclusion of carbohydrates in pre-workout strategies can significantly impact endurance, strength, and overall workout output. Adding glucose powder to the pre-workout drink is a very easy, effective and inexpensive method to gain better performance.
Benefits:
- Energy Reserves: Carbohydrates are the body’s preferred source of energy, especially during high-intensity exercises. Consuming carbohydrates before a workout can help top up glycogen stores, providing readily available fuel for muscle contractions.
- Sustained Performance: Including carbohydrates in your pre-workout routine can delay the onset of fatigue, allowing you to perform at a higher intensity for a longer duration.
- Muscle Preservation: When glycogen levels are optimized, the body is less likely to break down muscle tissue for energy, preserving hard-earned gains.
Risks and Considerations:
- Digestive Comfort: Choosing easily digestible carbohydrate sources can minimize the risk of gastrointestinal discomfort during workouts. Avoiding high-fibre and heavy meals close to exercise is advisable.
- Individual Tolerance: While carbohydrates are a crucial energy source, individual tolerance levels can vary. Some individuals may perform better with more carbohydrates, while others might benefit from a balanced approach.
Medical Considerations:
- Individuals with specific dietary restrictions, such as diabetes, may need to monitor carbohydrate intake closely and consult a healthcare provider before adjusting their pre-workout nutrition.
Safe Dosage:
- There isn’t a specific dosage for carbohydrates, as individual needs vary based on factors like exercise intensity, duration, and metabolic rate. Customizing carbohydrate intake to match your workout demands and personal preferences is key.
Natural Extracts: Harnessing Nature’s Power:
The realm of pre-workout compounds extends beyond traditional ingredients, incorporating the potency of natural extracts to optimize workout performance. From green tea extract to beetroot extract, these natural compounds offer a holistic approach to enhancing energy, endurance, and overall exercise outcomes.
Green Tea Extract:
- Metabolic Boost: Green tea extract contains compounds like catechins and caffeine, which have been linked to increased metabolism and fat oxidation. This can contribute to improved energy utilization during workouts.
- Antioxidant Support: The rich antioxidant content of green tea extract can help combat oxidative stress induced by intense exercise, potentially aiding in recovery.
Beetroot Extract:
- Nitric Oxide Boost: Beetroot extract is a rich source of dietary nitrates, which the body converts into nitric oxide. This process enhances blood vessel dilation, leading to improved blood flow and oxygen delivery to muscles.
- Endurance Enhancement: The nitric oxide boost from beetroot extract has been shown to enhance endurance by allowing muscles to work more efficiently and delay fatigue.
Other Natural Extracts:
- Adaptogenic Potential: Extracts from adaptogenic herbs like ginseng and ashwagandha can offer stress-reducing effects, indirectly improving exercise performance by regulating stress hormones.
- Performance-Enhancing Herbs: Certain herbs like cordyceps and rhodiola have been traditionally used to improve physical performance and reduce fatigue, making them intriguing additions to formulations.
Risks and Considerations:
- Standardization: When using natural extracts, ensuring that the product is standardized for active compounds is essential to guarantee consistent potency and effects.
- Allergies and Sensitivities: Some individuals might be sensitive or allergic to specific plant compounds. It’s advisable to start with a small dose and monitor your body’s response.
Medical Considerations:
- Individuals with specific allergies or sensitivities to plants should exercise caution and consult a healthcare provider before using natural extracts.
- Some natural compounds might interact with medications, emphasizing the importance of professional guidance.
- All that is natural is safe for health is a myth! Also, some of the herbal supplements and formulations may be harmful for the liver. It is important to exercise caution with such supplements
Safe Dosage:
- Dosages of natural extracts can vary based on the specific compound and intended effects.
- Consulting product labels, reputable sources, and healthcare professionals can help you determine appropriate dosages.
Tyrosine: Mental Focus and Stress Reduction:
Tyrosine is claimed to sharpen mental acuity and manage stress during workouts. This non-essential amino acid plays a pivotal role in the production of neurotransmitters that influence cognitive function and mood.
Benefits:
- Neurotransmitter Precursor: Tyrosine is a precursor to key neurotransmitters like dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. These chemicals regulate mood, focus, and stress response, making tyrosine a potential mental performance enhancer.
- Cognitive Focus: By boosting the availability of neurotransmitters associated with focus and concentration, tyrosine supplementation can help maintain mental clarity during demanding exercises.
- Stress Adaptation: Tyrosine’s influence on stress-related neurotransmitters can aid in managing the physiological response to stressors, potentially reducing the impact of workout-induced stress.
Risks and Considerations:
- Dosing Considerations: While tyrosine supplementation can be beneficial, higher dosages may not necessarily yield greater effects. Finding the optimal dosage for your needs is essential.
- Tolerance: Long-term use of tyrosine might lead to tolerance, reducing its perceived effects over time. Cycling its usage or consulting a healthcare provider can address this concern.
Medical Considerations:
- Individuals with bipolar disorder or those taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) should avoid tyrosine supplementation due to potential interactions.
- As tyrosine influences neurotransmitters, consulting a healthcare provider is advised for those with mood disorders or on medications affecting neurotransmitter levels, antidepressants etc.
Safe Dosage:
- Dosages typically range from 500 to 2,000 milligrams per day.
- Starting with a lower dosage and gradually increasing, while monitoring its effects, can help determine the right amount for you.
Also Read: Epilepsy & Nutrition
Betaine: Performance and Muscle Endurance:
As the world of pre-workout compounds continues to evolve, betaine emerges as a promising addition for individuals seeking to maximize their exercise performance and muscle endurance. Derived from sources like beets, this naturally occurring compound offers advantages that span both strength-focused and endurance-oriented activities.
Benefits:
- Strength and Power: Betaine’s potential to enhance muscle protein synthesis and promote cell hydration contributes to improved strength and power during resistance exercises. This is particularly beneficial for individuals engaged in weightlifting and explosive movements.
- Anaerobic Performance: Studies suggest that betaine may enhance anaerobic performance, allowing for sustained high-intensity efforts during activities like sprints and HIIT workouts.
- Muscle Endurance: By supporting cell hydration, betaine can delay muscle fatigue, potentially leading to prolonged workout capacity and enhanced muscle endurance.
Risks and Considerations:
- Individual Variation: Responses to betaine supplementation can vary among individuals, with some experiencing more pronounced effects than others.
- Digestive Tolerance: While generally well-tolerated, high doses of betaine might lead to gastrointestinal discomfort in some individuals.
Medical Considerations:
- Betaine is considered safe for healthy individuals. However, if you have any medical conditions, consulting a healthcare provider before supplementation is recommended.
Safe Dosage:
- Dosages typically range from 1,500 to 3,000 milligrams per day.
- Starting with a lower dosage and gradually increasing can help determine your optimal betaine intake.
HMB (Beta-Hydroxy Beta-Methylbutyrate): Muscle Preservation and Recovery:
HMB (Beta-Hydroxy Beta-Methylbutyrate) has gained recognition for its potential to support muscle preservation and facilitate recovery. This metabolite of the amino acid leucine offers unique advantages for individuals aiming to minimize muscle breakdown and optimize their post-workout repair process.
Benefits:
- Muscle Protein Synthesis: HMB’s role in promoting muscle protein synthesis supports the repair and growth of muscle tissue after intense workouts. This is particularly valuable for those engaged in resistance training and muscle-building pursuits.
- Muscle Preservation: By inhibiting muscle protein breakdown, HMB helps prevent the loss of hard-earned muscle mass during periods of calorie deficit or intense training.
- Reduced Muscle Damage: HMB’s anti-inflammatory properties can contribute to reduced muscle damage and soreness, leading to faster recovery and improved readiness for subsequent workouts.
Risks and Considerations:
- Dosage Variation: Effective dosages of HMB can vary based on individual goals and training intensity. Experimentation and monitoring your body’s response are key.
- Supplementation Duration: While short-term HMB supplementation is generally well-tolerated, prolonged use might lead to decreased effectiveness over time.
Medical Considerations:
- HMB is considered safe for healthy individuals. However, consulting a healthcare provider, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions, is advised before incorporating it into your regimen.
Safe Dosage:
- Effective HMB dosages typically range from 2 to 3 grams per day.
- Starting with the lower end of the dosage range and gradually increasing can help determine your optimal intake.
Conclusion: Navigating the Supplement Landscape with Pragmatism
In the world of fitness and supplements, the realm of pre-workout compounds is a mix of various ingredients that can boost your workout. We’ve explored basics like caffeine, beta-alanine, and citrulline. But there’s more to the story. Other ingredients like theacrine, Alpha-GPC, choline bitartrate, vitamin B6, and more also find their place. They’re said to enhance focus and cognition during workouts.
Amidst these claims, it’s crucial to approach pre-workout supplements with caution. The market is flooded with options, each promising rapid results. However, the reality is more nuanced. Creating an effective pre-workout routine involves careful choices and realistic expectations. The potential benefits of an ingredient might be impressive, but it’s important to know how it works for you.
Remember, pre-workout supplements are just a piece of the puzzle. Proper nutrition, hydration, rest, and consistent training are equally important.
The pursuit of improved performance is a nuanced journey that extends beyond a single pill or powder. While supplements have their place, they’re far from the sole answer to unlocking peak performance. A well-rounded approach encompassing nutrition, rest, and recovery is paramount for genuine progress. By blending knowledge, smart choices, and sensible decisions, you can navigate the world of pre-workout compounds effectively while staying grounded in a balanced fitness journey
- A Balanced Approach: Supplements, while often enticing, should never be viewed as magic bullets that replace the fundamentals of a balanced diet. The nutrients obtained from whole foods are the foundation upon which effective supplementation can build.
- Nutrition and Rest: Without proper nutrition, even the most acclaimed supplements can fall short. The body requires essential nutrients from a variety of sources to fuel workouts and support recovery. Equally vital is the role of rest and sleep in allowing muscles to recover and adapt.
- Cautious Consideration of Caffeine: While caffeine might offer a temporary energy boost, excessive consumption can lead to detrimental effects. It’s essential to recognize that the body’s tolerance to caffeine can develop, and its misuse can lead to sleep disturbances and heightened stress levels.
- Evolving Market and Claims: The supplement market is teeming with products that promise miraculous results, often backed by flashy marketing rather than scientific evidence. It’s imperative to approach new supplements with skepticism and seek claims that are substantiated by credible research.
- Evidence-Based Standouts: Amid the sea of supplements, a handful have demonstrated potential benefits with reasonable scientific support. Carbohydrates provide essential energy for workouts, creatine has a solid track record for strength and muscle gains, caffeine can temporarily enhance focus and energy, citrulline can aid in blood flow, and beta-alanine might delay fatigue during intense efforts.
- A Mindful Approach: As we conclude our exploration, it’s clear that a cautious, science-informed approach is crucial. No supplement can replace dedication, hard work, and consistency. By viewing supplements as enhancers rather than shortcuts, we can navigate this dynamic landscape while maintaining a balanced perspective on what truly fuels progress.
Improved performance is a holistic endeavour, determined by many factors such as training intensity, proper nutrition, restful sleep, and smart supplementation. The journey towards your fitness goals is uniquely yours, and a blend of knowledge, practicality, and self-awareness will guide you towards the results you seek
About NuvoVivo
NuvoVivo is an online health and fitness company that helps its client manage lifestyle diseases. Our clients join us from across the world to manage acidity or reverse conditions such as diabetes (and its complications), cardiovascular diseases (hypertension, high cholesterol), fatty liver, PCOS, thyroid disorders, IBS etc. We help them reduce their reliance on medications through structured and scientific lifestyle changes that suit their cultural habits and medical conditions. Our team provides a diet plan, exercise plans and the necessary follow-up and support to help them achieve this
Reach for Consultations @ https://bit.ly/NVConsultation
More about NuvoVivo @ https://linktr.ee/nuvovivo

