Vitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” is a fat-soluble vitamin essential for various important functions in the human body. Unlike other vitamins primarily obtained through diet, Vitamin D can be synthesized in the skin when exposed to sunlight. Inspite of living in a country where there is no dearth of sunlight, vit-d deficiency is very prevalent! According to a study in 2023 involving 2.2 lakh people across 27 cities in India, 3 out of every 4 Indians are deficient in Vitamin D. Or in other words, if you are an Indian, there is a 75% chance that you are deficient in Vit-D!
Vitamin D goes beyond just bone health and calcium absorption; it plays a multifaceted role in maintaining overall health. It regulates the expression of genes involved in immune function, modulates inflammation, and contributes to cell growth and differentiation. Adequate Vitamin D levels are also linked to reduced risks of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, certain cancers, and autoimmune disorders. Moreover, this vitamin is crucial for the maintenance of mental well-being. Low levels of Vitamin D is often associated with an increased risk of mood disorders and cognitive decline.
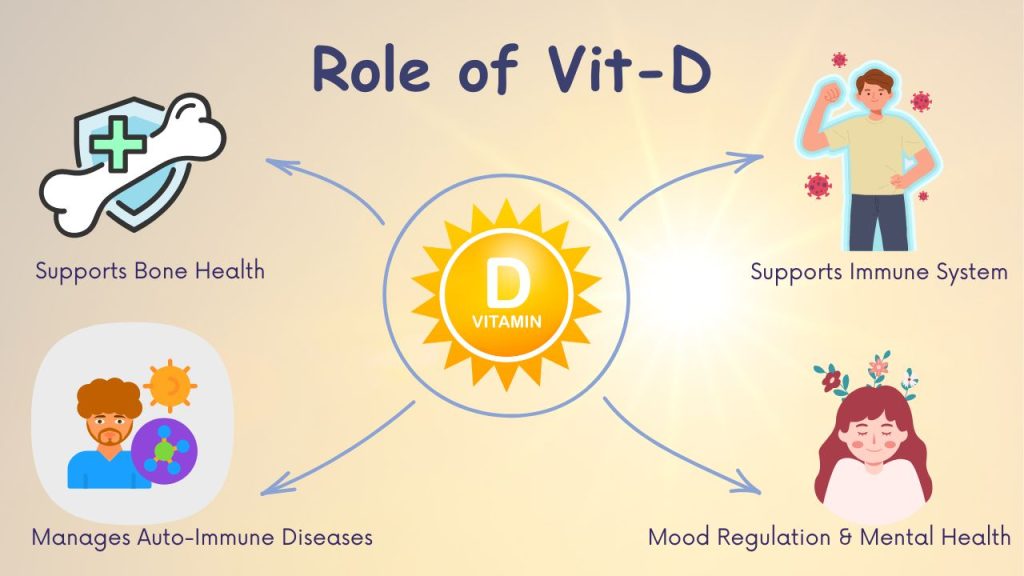
The Role of Vit D in the Body
Bone Health: Vitamin D’s most recognized role is in maintaining optimal bone health. It facilitates the absorption of calcium and phosphorus in the small intestine – essential for the formation and mineralization of bone. Deficiency in Vitamin D can hence lead to decreased calcium absorption, resulting in weakened bones, increased risk of fractures, osteoarthritis, and conditions such as rickets in children and osteoporosis & osteomalacia in adults.
Immune System Support: Beyond its role in skeletal health, Vitamin D is a crucial modulator of the immune system. It plays a role in both the innate and adaptive immune responses, influencing the function of various immune cells. Vitamin D is involved in the production of antimicrobial peptides and has anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to the body’s ability to defend against infections. Adequate Vitamin D levels are associated with a reduced risk of respiratory infections, autoimmune disorders, and other immune-related conditions.
Also Read: Autoimmune Diseases – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Lifestyle Changes
Managing Autoimmune Diseases: Vitamin D’s influence on the immune system extends to its role in modulating immune responses and preventing the development of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues in the body. Vitamin D helps regulate the immune response by suppressing excessive inflammation and promoting immune tolerance. Vitamin D promotes the function of regulatory T cells, which are responsible for preventing the immune system from attacking the body’s own cells.
Research suggests that adequate Vitamin D levels may reduce the risk of developing autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and lupus. Moreover, for those already diagnosed with autoimmune conditions, maintaining sufficient Vitamin D levels is extremely crucial to manage symptoms and potentially slow the progression of the disease.
Regulation of Mood and Mental Health: Emerging research suggests a significant link between Vitamin D levels and mental health. Vitamin D receptors are present in areas of the brain associated with mood regulation. Low Vitamin D levels have been linked to an increased risk of mood disorders such as depression and seasonal affective disorder (SAD). Furthermore, Vitamin D may play a role in cognitive function and is being studied for its potential impact on reducing the risk of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Sources of Vit-D
There are 2 types of Vitamin D – Vit-D2 (ergocalciferol) and Vit-D3 (cholecalciferol). Vit-D2 is derived from plant sources, fungi, yeast and mushrooms, whereas Vit-D3 is derived from animal sources. Vitamin D3 is the more effective form (biologically active), closely resembling the Vitamin D produced under the skin.
Studies suggest that Vitamin D3 is more effective at raising and maintaining blood levels of Vitamin D compared to Vitamin D2. It has a longer duration of action in the body and is generally considered to be the preferred form for supplementation.
The major natural source of Vit-D is Ultraviolet B radiations of sunlight, which converts cholesterol below the skin epidermis to Vit-D. When UV-B radiation of 290-315 nm falls on the skin, the cholesterol (7-dehydrocholesterol) is converted into Vit-D. However, Vit-D from the diet or from under the skin synthesised by UV rays is biologically inactive. It is changed to its active form through certain reactions that happen first in our liver and then in the kidneys.
In terms of food, fatty fish like salmon and mackerel are excellent sources of Vitamin D3. Other options include cod liver oil, egg yolks, red meat, liver and organ meat. In cases where individuals are unable to obtain sufficient Vitamin D from sunlight and diet, supplements are available. Vit D3-based supplements are most commonly used, as compared to Vit D2.
How is Vitamin D deficiency diagnosed?
Diagnosing Vitamin D deficiency typically involves a blood test to measure the levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D, the main circulating form of Vitamin D in the bloodstream. Blood tests can accurately assess the concentration of Vitamin D and classify individuals into different categories, such as deficient, insufficient, or sufficient. The recommended blood level for Vitamin D is often expressed as nanograms per millilitre (ng/mL) or nanomoles per liter (nmol/L).
Why do people fall deficient in Vit D?
Vit-D deficiency is common among people living in polluted cities as a majority of the Ultraviolet – B radiations do not reach the earth’s surface and are reflected from the atmosphere due to smoke, fog and pollutants.
Geographical variations in sunlight intensity also contribute to regional differences in Vitamin D levels. Northern regions, especially during the winter months, may experience reduced sunlight exposure, impacting the synthesis of Vitamin D in the skin. Areas with limited sunlight, such as those experiencing long winters or located at higher latitudes, pose challenges for sufficient sun exposure.
Despite being a sun-drenched country, a substantial portion of the Indian population experiences limited sunlight exposure due to factors such as indoor occupations, cultural practices, and clothing styles. The majority of the Indian population also has higher levels of melanin in their skin, which provides protection against the harmful effects of excessive sunlight but also reduces the skin’s ability to produce Vitamin D in response to sunlight. Individuals with darker skin may require more extended sun exposure to generate sufficient Vitamin D. The application of sunscreen also reduces the Vit-D levels in the body, for the same reason. Note that Ultraviolet B radiation does not penetrate through glass – hence sunlight exposure indoors through glass doors and windows is not helpful for Vit-D synthesis.
Further, traditional Indian diets (which itself varies across the geography) do not always include sufficient amounts of Vit-D rich food. Fatty fish, which is a good source of Vitamin D, may not be a staple in all regions and diets. A vegetarian diet, common among Indians, also poses a challenge in obtaining adequate Vitamin D. Certain cultural practices, such as avoiding direct sunlight due to concerns about skin darkening, also contribute to reduced sunlight exposure and, consequently, lower Vitamin D levels.
Such lifestyle aspects are the most common reason for low vit-d levels among Indians. However, in some individuals, certain health conditions also can lead to low vitamin D levels. Health conditions affecting the absorption of dietary fat, such as celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and certain gastrointestinal disorders, can lead to impaired absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, including Vitamin D.
Kidney and liver diseases also can cause low Vitamin D levels as it impair the conversion of Vit-D into its active form. Certain autoimmune conditions, such as lupus and multiple sclerosis are often associated with lower Vitamin D levels. Overactivity of the parathyroid glands (hyperparathyroidism) is yet another medical condition, that can lead to increased breakdown of bone tissue, releasing calcium into the bloodstream and potentially decreasing Vitamin D levels. For those grappling with low vitamin D levels due to such medical conditions, it is crucial to supplement them only based on your doctor’s advice!
Sunlight Exposure & Safety Guidelines
Ensuring optimal Vitamin D synthesis while maintaining skin health requires a delicate balance. Guidelines recommend spending a moderate amount of time outdoors during peak sunlight hours without sunscreen. The duration varies based on many factors like skin type (melanin content), any existing skin conditions, geographic location, and time of the day.
As far as India is concerned, exposure of arms, legs, or the face for 10 to 30 minutes, between 10 am to 3 pm, two to three times a week, may contribute to adequate Vitamin D synthesis for most of us.
However, it’s crucial to practice sun safety by avoiding excessive sun exposure to prevent skin damage and reduce the risk of skin cancer. After the recommended exposure time, applying sunscreen or protective clothing is important.
Also Read: Cancer & Lifestyle Management
Risk of Over-Supplementation
While Vitamin D supplementation is often recommended to address deficiencies, excessive intake can lead to health risks – some of them very dangerous to life. Over-supplementation of Vitamin D can lead to increased calcium absorption, resulting in elevated levels of calcium in the blood. This can disrupt the normal electrical signalling in the heart, leading to irregular heartbeats or arrhythmias and manifest as palpitations, rapid heart rate, or other abnormal heart rhythms.
Calcium is essential for the contraction and relaxation of heart muscles. Excessive calcium can interfere with these processes, affecting the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. It may also lead to calcification of blood vessels – a process associated with atherosclerosis (plaque/block in arteries)
It can also cause calcification of soft tissues including heart valves, lungs, kidneys and brain – a condition known as ectopic calcification. High doses of Vitamin D may cause digestive issues and abdominal discomfort such as nausea, vomiting, and constipation. Increased levels of calcium also increase the chance of kidney stones and kidney damage.
Excess Vit-D levels in the body often happen with unscrupulous supplementation, and not through normal dietary/food sources. Those who are at risk of falling deficient in Vit-D levels are advised to follow the advice of a qualified health practitioner before consuming supplements. The appropriate dosage and frequency need to be adjusted to your lifestyle, health and current Vit-D levels.
How can we help?
Health, fitness & wellness are intricately linked to the choices we make in our daily lives. At the heart of this is the importance of a balanced meal, incorporating adequate protein, fats, and carbohydrates. It’s crucial not to glorify one nutrient over the others or demonize any, as each plays a unique role in our overall well-being. Tailoring these nutrients based on individual parameters such as medical conditions and age is key to achieving optimal health.
Micronutrients, found in abundance in vegetables and fruits, are equally vital. A balanced approach ensures the body receives essential vitamins and minerals, contributing to overall vitality.
In the realm of exercise, the trio of cardio, weight training, and yoga each holds its own significance. Just as with macronutrients, there’s no one-size-fits-all when it comes to workouts. A harmonious blend, tailored to individual needs, contributes to holistic well-being.
Ultimately, achieving health and wellness involves carefully balancing nutrients, engaging in diverse exercises, and managing stress while prioritizing quality sleep. Our comprehensive approach helps clients strike this balance, enhancing metabolism, improving body composition with increased muscle mass, and effectively reversing the aging process. Join us on the journey to holistic health and well-being, where every choice brings you closer to a more vibrant and resilient you.
Wellness Begins Here! Take Charge Now!
Join us @ https://www.nuvovivo.com/pricing/

